What is a population?;A group of individuals of a single species living in same general read ;Population_Ecology
What is population density?;\(density = \frac{# individuals}{area}\) ;Population_Ecology
What is random dispersal?;Unpredicatable spacing, not as commin in nature ;Population_Ecology
What is uniform dispersal?;Usually antagonistic interactions, all organisms are equadistant ;Population_Ecology
What is clumped dispersal?;Organisms are clumped together, with large amounts of space between clumps ;Population_Ecology
What are survivorship curves?;A graph that indicates the proportion of offspring born to those that actually survive.  ;Population_Ecology
What are k selected species?;The are large in size. Sexual maturity is later in life. Produce few, large, immature offspring. Offspring receive lots of perantal care. Intraspecific competition is high.
;Population_Ecology
What are k selected species?;The are large in size. Sexual maturity is later in life. Produce few, large, immature offspring. Offspring receive lots of perantal care. Intraspecific competition is high.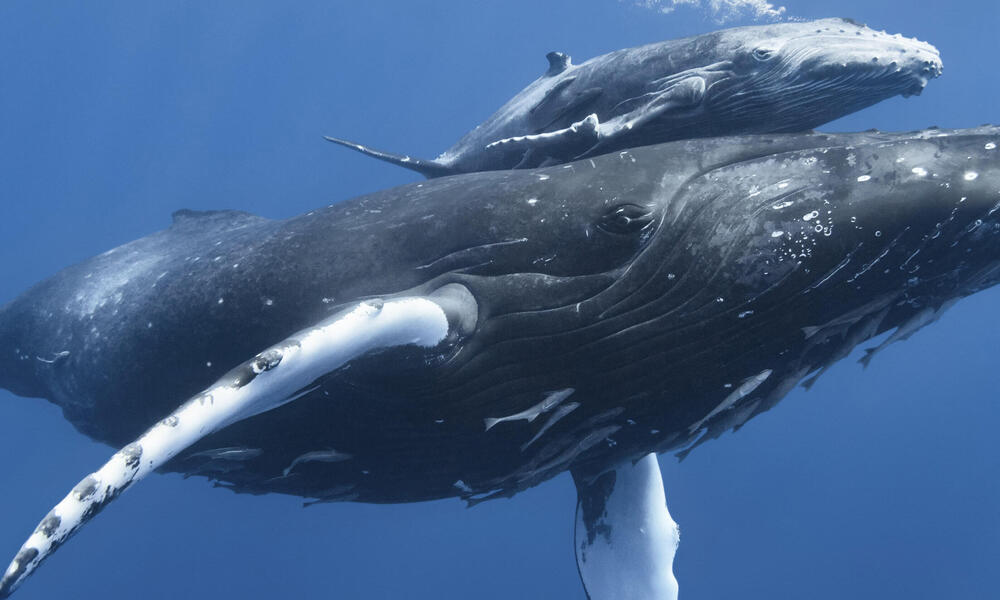  ;Population_Ecology
What are r selected species?;The opposite of k selection. Organisms are small in size. Early sexual maturity. Produce large numbers of small mature offspring. Little parental care. Intraspecific competition is low. ;Population_Ecology
What types of population growth is there?;Exponential and logistical growth ;Population_Ecology
What conditions create exponential growth?;Unlimited resources. No predators. No competition ;Population_Ecology
What is the formula for exponential population growth?;\(\frac{dN}{dT}=B-D=r_max N\), Change in number over change in time = Births - deaths = Per capita rate of increase x number of individuals.
;Population_Ecology
What are r selected species?;The opposite of k selection. Organisms are small in size. Early sexual maturity. Produce large numbers of small mature offspring. Little parental care. Intraspecific competition is low. ;Population_Ecology
What types of population growth is there?;Exponential and logistical growth ;Population_Ecology
What conditions create exponential growth?;Unlimited resources. No predators. No competition ;Population_Ecology
What is the formula for exponential population growth?;\(\frac{dN}{dT}=B-D=r_max N\), Change in number over change in time = Births - deaths = Per capita rate of increase x number of individuals.
Represents unrestrained growth, does not account for carrying capacity. 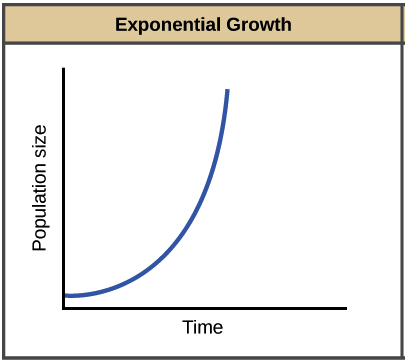 ;Population_Ecology
What is carrying capacity?;The max number of individuals and environment can support ;Population_Ecology
What is the formula for logistic growth?;\(\frac{dN}{dT}=r_max(\frac{K-N}{K})\). Change in number over change in time = per capita rate of increase * the unused portion of carrying capacity. ;Population_Ecology
What are limiting factors?;Constraints that prevent a population from reaching maximum growth. Limited space, food, etc ;Population_Ecology
What are density-dependent factors?;Any biotic limiting factors. Competition, diseases. ;Population_Ecology
What are density-independent factors?;Any abiotic limiting factors. Natural disasters, hurricanes, flood. ;Population_Ecology
;Population_Ecology
What is carrying capacity?;The max number of individuals and environment can support ;Population_Ecology
What is the formula for logistic growth?;\(\frac{dN}{dT}=r_max(\frac{K-N}{K})\). Change in number over change in time = per capita rate of increase * the unused portion of carrying capacity. ;Population_Ecology
What are limiting factors?;Constraints that prevent a population from reaching maximum growth. Limited space, food, etc ;Population_Ecology
What are density-dependent factors?;Any biotic limiting factors. Competition, diseases. ;Population_Ecology
What are density-independent factors?;Any abiotic limiting factors. Natural disasters, hurricanes, flood. ;Population_Ecology ;Population_Ecology
What are k selected species?;The are large in size. Sexual maturity is later in life. Produce few, large, immature offspring. Offspring receive lots of perantal care. Intraspecific competition is high.
;Population_Ecology
What are k selected species?;The are large in size. Sexual maturity is later in life. Produce few, large, immature offspring. Offspring receive lots of perantal care. Intraspecific competition is high.  ;Population_Ecology
What are r selected species?;The opposite of k selection. Organisms are small in size. Early sexual maturity. Produce large numbers of small mature offspring. Little parental care. Intraspecific competition is low. ;Population_Ecology
What types of population growth is there?;Exponential and logistical growth ;Population_Ecology
What conditions create exponential growth?;Unlimited resources. No predators. No competition ;Population_Ecology
What is the formula for exponential population growth?;\(\frac{dN}{dT}=B-D=r_max N\), Change in number over change in time = Births - deaths = Per capita rate of increase x number of individuals.
;Population_Ecology
What are r selected species?;The opposite of k selection. Organisms are small in size. Early sexual maturity. Produce large numbers of small mature offspring. Little parental care. Intraspecific competition is low. ;Population_Ecology
What types of population growth is there?;Exponential and logistical growth ;Population_Ecology
What conditions create exponential growth?;Unlimited resources. No predators. No competition ;Population_Ecology
What is the formula for exponential population growth?;\(\frac{dN}{dT}=B-D=r_max N\), Change in number over change in time = Births - deaths = Per capita rate of increase x number of individuals. ;Population_Ecology
What is carrying capacity?;The max number of individuals and environment can support ;Population_Ecology
What is the formula for logistic growth?;\(\frac{dN}{dT}=r_max(\frac{K-N}{K})\). Change in number over change in time = per capita rate of increase * the unused portion of carrying capacity. ;Population_Ecology
What are limiting factors?;Constraints that prevent a population from reaching maximum growth. Limited space, food, etc ;Population_Ecology
What are density-dependent factors?;Any biotic limiting factors. Competition, diseases. ;Population_Ecology
What are density-independent factors?;Any abiotic limiting factors. Natural disasters, hurricanes, flood. ;Population_Ecology
;Population_Ecology
What is carrying capacity?;The max number of individuals and environment can support ;Population_Ecology
What is the formula for logistic growth?;\(\frac{dN}{dT}=r_max(\frac{K-N}{K})\). Change in number over change in time = per capita rate of increase * the unused portion of carrying capacity. ;Population_Ecology
What are limiting factors?;Constraints that prevent a population from reaching maximum growth. Limited space, food, etc ;Population_Ecology
What are density-dependent factors?;Any biotic limiting factors. Competition, diseases. ;Population_Ecology
What are density-independent factors?;Any abiotic limiting factors. Natural disasters, hurricanes, flood. ;Population_Ecology